Expressvpn Glossary
Data warehouse
What is a data warehouse?
Data warehouses are centralized systems that store and manage large volumes of structured data.
These systems collect data from multiple sources and organize it for analysis, reporting, and long-term storage. Administrators use data warehouses to gain insights and optimize decision-making.
How does a data warehouse work?
Data warehouses typically rely on Extract, Transform, Load (ETL) pipelines to facilitate the movement of data. To increase efficiency, information is extracted from a system and transformed into a consistent format before being loaded into the warehouse.
In terms of structure, data warehouses generally use either a star or a snowflake schema and are built around fact and dimension tables.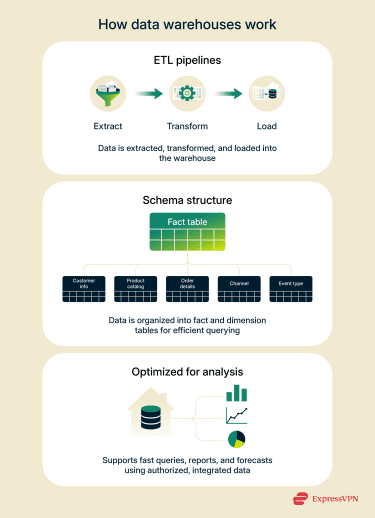 Data warehouses are optimized for large-scale aggregation and reporting tools. They generally handle internal data and information from authorized sources.
Data warehouses are optimized for large-scale aggregation and reporting tools. They generally handle internal data and information from authorized sources.
Data warehouse vs. database
Databases are built to handle everyday tasks like recording transactions, updating inventory, and automating processes. Data warehouses are designed to support analysis, such as finding sales trends or predicting future demand.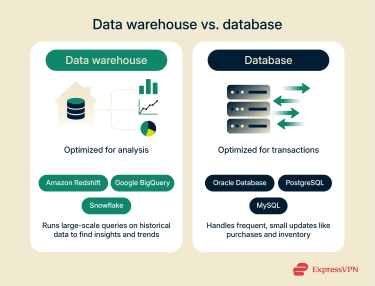 Databases prioritize speed and reliability and tend to deal with frequent, small transactions. Data warehouses focus on handling queries across vast amounts of historical data, with performance tuned for complex analysis rather than transaction speed.
Databases prioritize speed and reliability and tend to deal with frequent, small transactions. Data warehouses focus on handling queries across vast amounts of historical data, with performance tuned for complex analysis rather than transaction speed.
Common use cases
Data warehouses are primarily used for business intelligence reporting. They play a key role in helping organizations perform analytics to optimize performance and refine strategies.
Real-world examples of data warehouses
The platforms below are often used by organizations in finance, retail, healthcare, and technology to process large datasets for business intelligence and decision-making.
- Amazon Redshift: Widely used for scalable analytics in enterprise environments.
- Google BigQuery: Serverless warehouse designed for high-speed querying.
- Snowflake: Flexible service used for large-scale data operations.
Further reading
FAQ
Is a data warehouse the same as a database?
No, a data warehouse isn’t the same as a database. While databases handle everyday transactional tasks such as recording purchases or updating inventory, data warehouses are designed for analytical processing.
What is an example of a data warehouse?
Examples of data warehouses include Amazon Redshift, Google BigQuery, and Snowflake. These platforms are widely used in enterprise environments to consolidate data from multiple sources, optimize large-scale queries, and provide insights for business intelligence and analytics.
What industries use data warehouses?
Data warehouses are used across many industries, including finance, retail, telecommunications, and healthcare. Organizations in these sectors rely on them to analyze behavior, assess operations, track performance metrics, and improve strategic decision-making.
How is a data warehouse different from a data lake?
A data warehouse differs from a data lake in how it stores and organizes data. Data warehouses store structured data in predefined schemas for analytics and reporting, whereas data lakes can hold structured and unstructured data in raw form, offering more flexibility but less optimization for traditional analysis.
