Expressvpn Glossary
Data lake
What is a data lake?
A data lake is a central repository that can store huge amounts of data. It can hold all types of data, including structured (like spreadsheets), semi-structured (like XML or JSON files), and unstructured (like text documents, images, and videos).
How does a data lake work?
The key concept behind a data lake is schema-on-read. This means the data's structure isn’t defined when it's stored but is only applied at the time of analysis, which allows data lakes to handle a wide variety of data types without upfront modeling.
The data lake process includes:
- Ingestion: Collects large volumes of structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data from various sources.
- Raw storage: Stores all data in its original, unprocessed format.
- Management: Uses metadata, indexing, and governance controls to keep data secure and findable.
- Analysis: Allows users to query raw data using big data tools like Apache Spark or Hadoop and query engines like Presto.
Data lake vs. data warehouse
Data lakes hold raw, uncurated data of all kinds. They’re well suited to artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) training, and to open-ended exploration.
Data warehouses, on the other hand, are central repositories for curated data, typically structured or semi-structured, that’s optimized for business intelligence. They use high-performance databases to deliver fast, low-latency queries for historical analysis and reporting.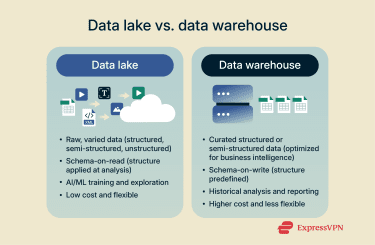 Unlike data lakes, which use the schema-on-read approach, warehouses use schema-on-write, meaning all data has a consistent schema applied to it as it’s written to storage.
Unlike data lakes, which use the schema-on-read approach, warehouses use schema-on-write, meaning all data has a consistent schema applied to it as it’s written to storage.
In terms of cost, data warehouse storage often costs more and is less flexible than low-cost object storage in data lakes.
Benefits of data lakes
Organizations implement data lakes for several reasons, including:
- Centralized, scalable storage: Data lakes can eliminate data silos.
- Flexibility: Lakes accommodate any data format without a predefined schema.
- ML and AI support: Raw data provides a strong foundation for advanced analytics.
- Lower costs: Data lakes use economical cloud object storage instead of more expensive warehousing.
Common use cases and examples
Data lakes power various applications across industries, including:
- ML: Data scientists use massive datasets to train algorithms that predict customer behavior, detect fraud, or forecast demand.
- Internet of Things (IoT) data collection: Data lakes ingest and store continuous streams of sensor data for pattern analysis and anomaly detection.
- Security monitoring: Organizations collect log files and network traffic data to identify security threats and investigate incidents.
- Log and event storage: Application logs, system events, and audit trails are stored for troubleshooting and compliance.
Leading cloud providers offer popular data lake solutions, including Amazon S3-based data lakes and Azure Data Lake Storage. These platforms are used to store and analyze diverse data in industries like finance (for fraud detection), healthcare (to improve patient care), and tech (for predictive maintenance).
Further reading
FAQ
What are common tools for building a data lake?
Popular tools include Apache Spark for processing and transforming data, Presto for querying, Apache Kafka for real-time data ingestion, and object storage on Amazon S3 or Azure Data Lake Storage.
What industries use data lakes?
Healthcare uses data lakes for patient records and imaging. Financial service firms rely on them for risk analysis and fraud detection, while retail companies aggregate customer data for personalization. Technology companies store user logs, and manufacturing businesses collect Internet of Things (IoT) sensor data for predictive maintenance.
Does a data lake store structured data?
Yes, a data lake can store structured data. However, the primary advantage of data lakes is their ability to store and process unstructured and semi-structured data as well, without needing a predefined schema.
