Expressvpn Glossary
Dark Web

What is the dark web?
The dark web is a part of the internet that isn’t indexed by standard search engines like Google or Bing. It exists on encrypted networks, most notably the Tor (short for The Onion Router) network, that require special software or configurations to access.
While the dark web is often associated with illegal activity (such as illicit marketplaces or forums), it also supports legitimate uses, such as protecting privacy, fighting censorship, and enabling secure communication for whistleblowers, journalists, and activists.
How does the dark web work?
Accessing the dark web typically involves connecting through Tor, a privacy network designed to conceal both identifying information and the websites being visited. Internet traffic is routed through three relays: an entry node, a middle node, and an exit node. Each relay peels off one layer of encryption, ensuring that no single node can see both the origin and the destination of the traffic.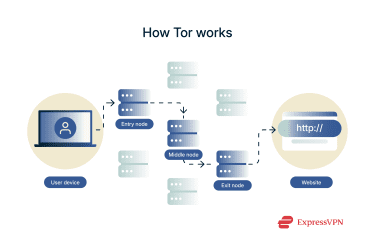 Websites on the dark web use addresses ending in .onion, which are not listed in public domain registries and cannot be opened in standard browsers. These addresses rely on Tor’s internal routing system and must be accessed through Tor-enabled tools like the Tor Browser.
Websites on the dark web use addresses ending in .onion, which are not listed in public domain registries and cannot be opened in standard browsers. These addresses rely on Tor’s internal routing system and must be accessed through Tor-enabled tools like the Tor Browser.
Most dark web sites aren’t indexed by a central search engine. To find them, it usually takes knowing the address in advance or browsing curated directories shared in trusted communities.
Because traffic is encrypted and split across multiple hops, tracking individuals or site owners becomes extremely difficult. Still, the network isn’t foolproof. Accessing dark web sites while logged into personal accounts, reusing breached credentials, or downloading unverified files can still lead to deanonymization.
Why is it important?
The dark web offers privacy in places where privacy doesn’t exist. In countries with heavy surveillance, censorship, or political risk, it allows people to publish information, securely access restricted content, and communicate without exposing their real identity.
Unlike mainstream platforms that tie activity to names, phone numbers, or IP addresses, dark web networks like Tor disconnect online actions from individuals. There is a caveat, though: internet service providers (ISPs) can still see when someone accesses the dark web.
The dark web is also important in the context of personal security. That’s because when companies are breached, the stolen data often surfaces in hidden forums on the dark web. These are not indexed, moderated, or removed. In fact, these forums exist specifically to circulate information others want kept private. Passwords, email addresses, phone numbers; anything leaked may end up there. Knowing about these risks makes it easier to take preventive steps, like setting up two-factor authentication (2FA), and respond in the right way in case of a breach, such as by promptly changing passwords across accounts.
Where is it used?
The dark web can be accessed from anywhere with an internet connection, but in practice, it’s often used in environments where regular internet access is restricted or monitored, such as regions with heavy surveillance, active conflict zones, or strict censorship laws. In these contexts, it offers a way to access information and communicate more privately, without relying on platforms that track identity or activity.
The dark web also supports more private browsing, communication, or file sharing, helping reduce the digital footprint left behind.
Further reading
- Dark web scan: Is your personal data at risk?
- Deep web vs. dark web: What’s the difference?
- What to do if your information is on the dark web
FAQ
Is it illegal to view the dark web?
No. Accessing the dark web or visiting .onion sites with a tool like Tor is legal in most countries. What’s illegal is using it for criminal activity, like buying illicit goods or sharing prohibited content.
Can police track you on the dark web?
Tracking people on the dark web is difficult, but not impossible. Tor is designed to hide identities, but mistakes, malware, or targeted operations can still reveal them. Law enforcement has successfully deanonymized individuals involved in serious crimes.
What does it mean to be found on the dark web?
Being found on the dark web usually means personal data (like a password or ID number) was leaked in a breach and listed for sale. It doesn’t mean the individual visited the dark web.
What’s the free dark web browser for iPhone?
The Onion Browser is a free iOS app that lets people access .onion sites through the Tor network. It’s open source and works with tools like Orbot to increase privacy.
What’s the difference between the dark web and Tor?
Tor is a privacy-focused network that routes internet traffic through a series of encrypted relays to keep identities and activity private. It allows access to both the regular internet (the surface web) privately, as well as to the dark web.
The dark web refers to hidden websites that use Tor-specific domains (typically ending in .onion) and are only accessible through Tor or compatible software. These sites are not indexed by traditional search engines and are hosted within the Tor network itself.
Why can’t the dark web be shut down?
The dark web can’t be shut down because it’s decentralized. It runs on a global network of servers with no central control. While law enforcement can take down individual dark web sites, typically by locating and seizing the physical servers or through operational security flaws, the underlying infrastructure (like the Tor network itself) remains fully functional and widely distributed. As long as the Tor network is running and people continue to host hidden services, the dark web will persist.
