What is a MAC address and why does it matter?
A Media Access Control (MAC) address is a unique identifier that helps your device connect to and communicate on a local network. Whenever your phone, laptop, or smart gadget joins Wi-Fi or pairs with another device, it shares this address to identify itself on that network.
Because MAC addresses are visible on local networks, they can reveal patterns that advertisers or trackers might use. Knowing where to find it and how to randomize your MAC address can help limit tracking and make your network activity harder to profile.
What is a MAC address?
A MAC address is a unique identifier that every network-capable device carries. It acts like a digital name tag that helps your phone, laptop, or smart gadget communicate on a local area network (LAN). They’re almost never used on the internet, where IP addresses are mainly displayed to identify devices.
Because a MAC address is embedded in your device’s network hardware, it plays a key role in managing communication between your device and nearby routers, switches, or other connected devices.
Why MAC addresses matter in networking
MAC addresses uniquely identify devices on a local network, allowing switches and Wi-Fi routers to deliver data to the right destination. Protocols like the Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) map IP addresses to MAC addresses, helping devices recognize each other and communicate correctly.
In some networks, MAC addresses are used as a simple access control mechanism. Administrators can restrict connections to a list of approved MAC addresses. However, this method provides minimal security because MAC addresses can be easily copied or spoofed.
MAC address vs. IP address: Key differences
The table below highlights the main distinctions between MAC and IP addresses:
| MAC address | IP address | |
| What it identifies | Identifies the physical network hardware in your device | Identifies your device on the wider internet or local network |
| Assignment | Permanently assigned to your device’s network interface | Assigned dynamically or statically by the network you connect to |
| Scope of communication | Used for communication within a local network | Used for communication across local and wide area networks, including the internet |
| Function | Helps switches and routers send data to the correct hardware | Helps data travel between different networks and online services |
How do MAC addresses work?
A MAC address acts like a label that helps your device take part in local network communication. When your device sends data, the network includes the MAC address so switches know exactly where the information should go.
How MAC addresses are assigned
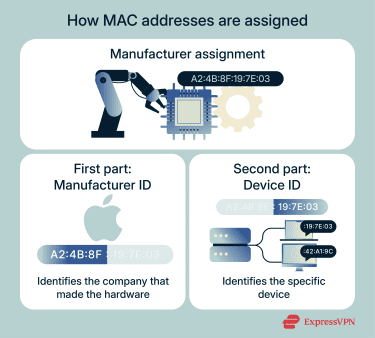 Manufacturers assign MAC addresses to network hardware during production. Each device receives a unique value so it can be identified on any local network.
Manufacturers assign MAC addresses to network hardware during production. Each device receives a unique value so it can be identified on any local network.
A MAC address has two parts:
- The first part of the MAC address identifies the manufacturer of the hardware.
- The second part is a unique number assigned by the manufacturer to differentiate each device.
This system allows millions of devices to operate without overlapping addresses, keeping local networks running smoothly.
MAC address structure and formats
A MAC address typically appears as six pairs of characters, most commonly separated by colons or hyphens. Each pair is written in hexadecimal, using digits 0–9 and letters A–F.
The first three pairs form the Organizationally Unique Identifier (OUI), which identifies the manufacturer. The last three pairs are assigned by the manufacturer to identify a specific network interface. This standardized format helps networks read addresses quickly and route data without confusion.
Here are some examples of valid MAC address formats:
- 00:1A:2B:3C:4D:5E.
- F4-12-FA-89-00-7C.
- A0B1C2D3E4F5 (no separators, common in some systems).
- 001A.2B3C.4D5E (Cisco-style grouping).
Do MAC addresses change?
Every network interface has a permanent, hardware-assigned MAC address that normally stays the same for the life of the device. Modern operating systems, however, can generate randomized MAC addresses to improve privacy. These temporary values help reduce tracking because networks see a changing identifier instead of the fixed hardware one.
The real MAC address still exists in the device, but the system uses the randomized version for most public or untrusted connections unless a network specifically requires the real hardware address.
Risks of exposing your MAC address
MAC addresses can be used to identify your device, monitor its activity, or match it to a specific manufacturer. In public places, the data can give network operators or attackers more insight into how often you connect or which access points you use.
Can you be tracked by your MAC address?
You can be tracked within the same local network because the MAC address stays the same unless changed. This allows someone to follow your device's presence as long as you stay within that network. However, tracking isn’t possible beyond that LAN since MAC addresses don’t travel across the wider internet.
MAC address vulnerabilities and threats
On open networks, attackers can collect MAC addresses to map devices or analyze network behavior. Various tools can scan networks and compile lists of connected devices by their MAC addresses, aiding targeted attacks.
Additionally, public databases and projects collect MAC addresses observed in different locations worldwide. These initiatives show how logging exposed MAC addresses can potentially monitor device presence or movement over time.
Network disruptions and impersonation risks
If someone copies your MAC address, they can impersonate your device on the same local network. When two devices share the same MAC address, the router or switch won’t know which one to send data to, often causing connection drops or unstable performance. MAC spoofing can also bypass simple MAC-based filters found on older or unmanaged routers.
One related threat is ARP poisoning, where an attacker sends falsified ARP messages to link their MAC address to the IP address of another device. This allows them to intercept, modify, or block data intended for that device, potentially leading to man-in-the-middle (MITM) attacks or network disruptions.
These attacks are more likely on public Wi-Fi networks in cafes, airports, open hotels, or older office Wi-Fi systems. While MAC spoofing and ARP poisoning don’t expose personal data by themselves, they can cause confusion, temporary outages, or unauthorized access.
How to find your MAC address
Every operating system stores the MAC address in its network settings. The steps differ across platforms, but the address always appears next to your connection details. Some devices may show multiple MAC addresses or randomized values, but you can still find them without any special tools.
Windows
- Open the Start menu and select Settings.
- Choose Network & Internet.
- Pick Wi-Fi for wireless or Ethernet for wired connections.
- Click Hardware properties.
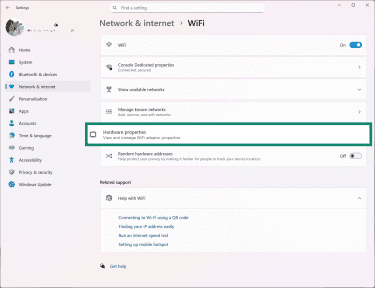
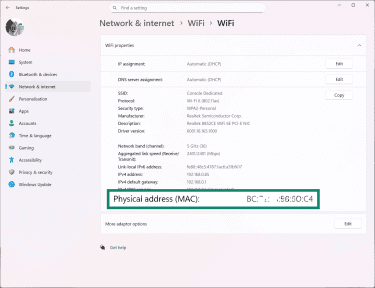
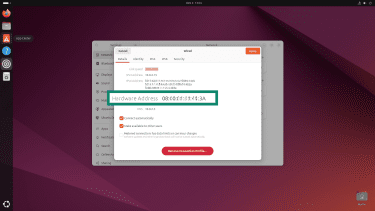
- Find the line labeled Physical address (MAC).
macOS
- Click the Apple menu and open System Settings.
- Select Network from the sidebar.
- Choose your active connection, such as Wi-Fi or Ethernet.
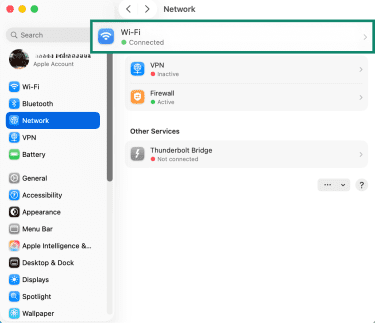
- Click Details or Advanced.
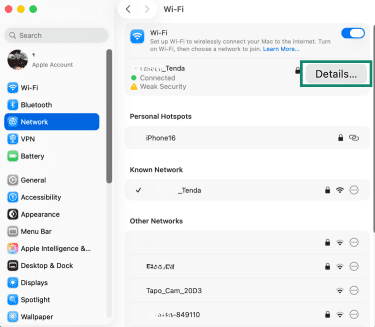
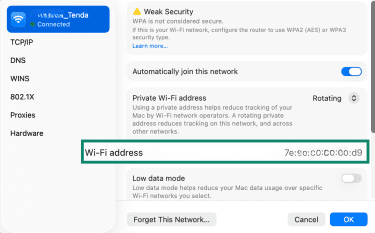
- Find the field called Wi-Fi Address or MAC Address.
Linux
- Open the Settings app.

- Go to Network, select your active connection, and click the cog icon to open its settings.
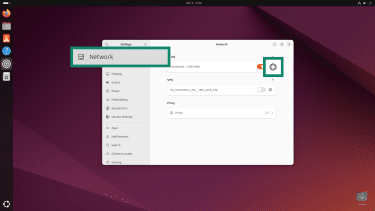
- Look for Hardware address or MAC Address in the connection details.
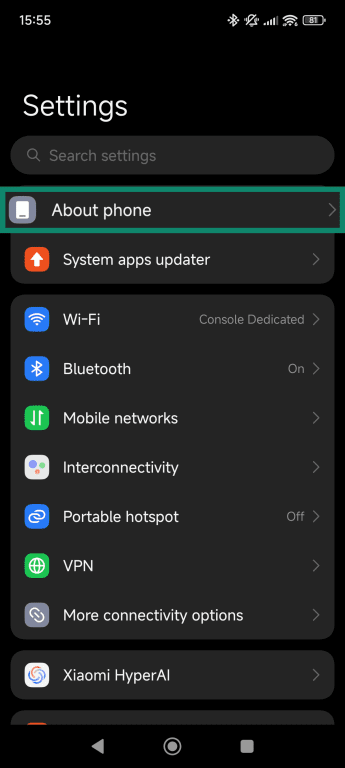
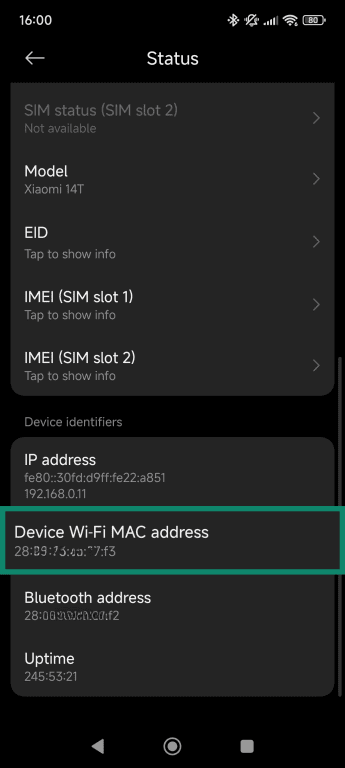
Android devices
- Open the Settings app and tap About Phone or About, depending on your device’s OS.
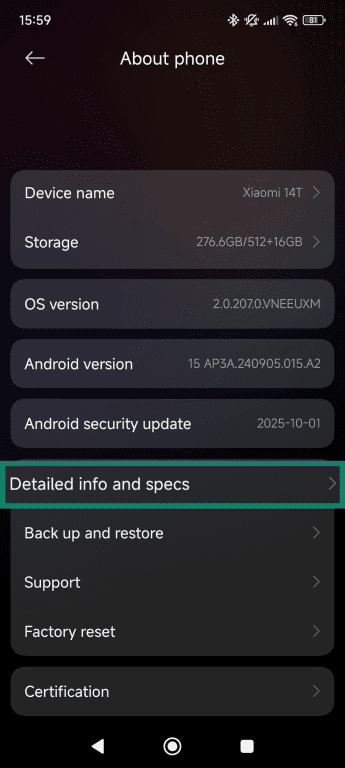
- Scroll down and select Detailed info and specs.
- Scroll down and select Status.
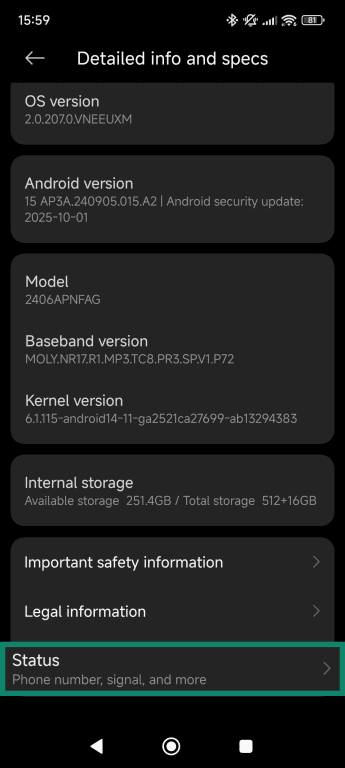
- Once inside, scroll down to view your Device Wi-Fi MAC address.
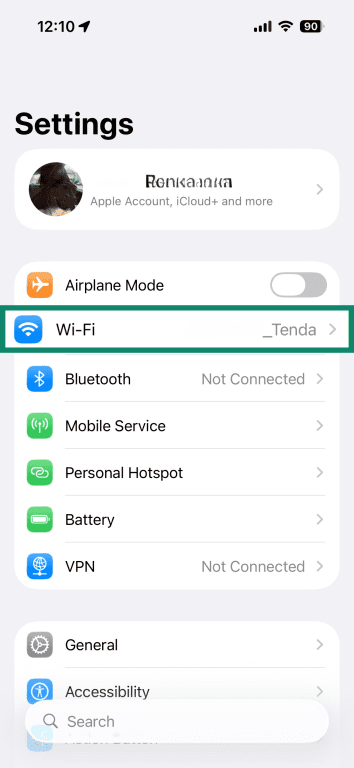
iOS
- Open the Settings app and tap Wi-Fi.
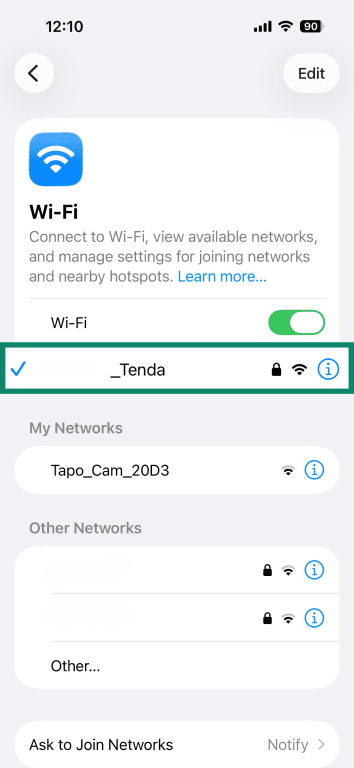
- Tap the "i" button next to the network you are connected to.
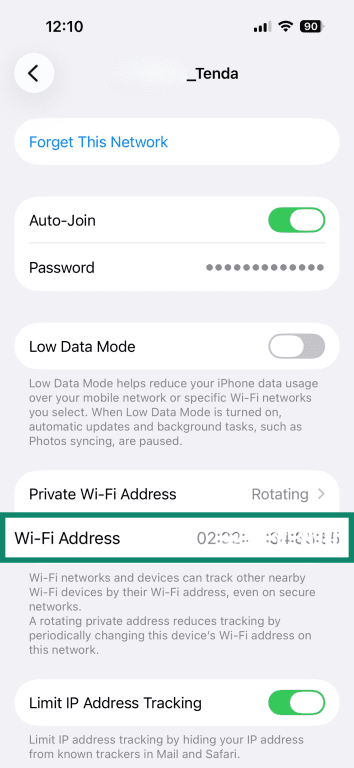
- Your device’s MAC address is listed next to Wi-Fi Address.
Can you change your MAC address?
You usually can’t permanently change a device’s factory MAC address because it’s stored in the Network Interface Card (NIC) firmware, although some specialized hardware does allow reprogramming.
Most operating systems, however, let you spoof or randomize the MAC address temporarily, causing the device to broadcast a different value on the network. This change affects only the active, software-configured address; the original hardware MAC remains unchanged in the background.
How to randomize a MAC address
Randomizing your MAC address can protect your privacy by changing the visible MAC address when connecting to Wi-Fi networks, making it harder to track your device.
Windows
- In Network & Internet, access your active network settings (Wi-Fi or Ethernet), and turn on Random hardware addresses.
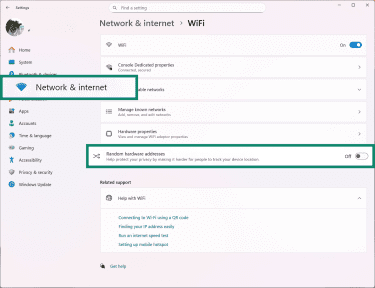
macOS
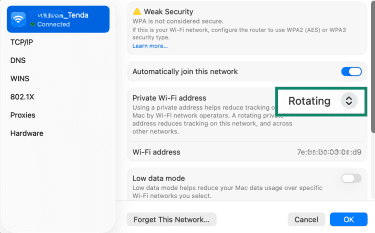
- In System Settings, open Network settings, choose your active network (Wi-Fi or Ethernet), and click the Advanced or Details button (steps 1–4 here).
- In the Private Wi-Fi Address field, select Rotating.
Linux
- Go to Network, select your active connection, and click the gear icon to open its settings.
- Click on the Identity tab.
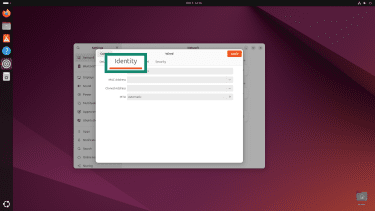
- Select your MAC address.
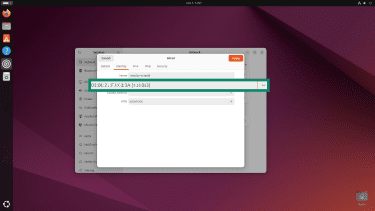
- In the Cloned Address field, select Random and click Apply.
Android
Note that changing the MAC address on Android depends on the device. Most versions allow temporary randomization but not full manual changes.
- Open Settings and select Wi-Fi or Network & Connections.
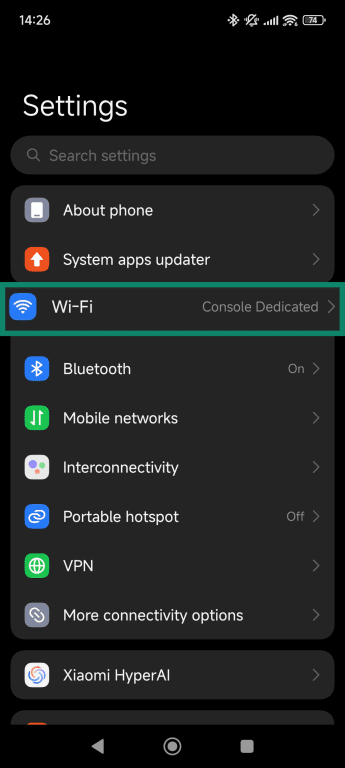
- Tap on the arrow icon next to your connected network.
- Find Privacy or MAC address type.
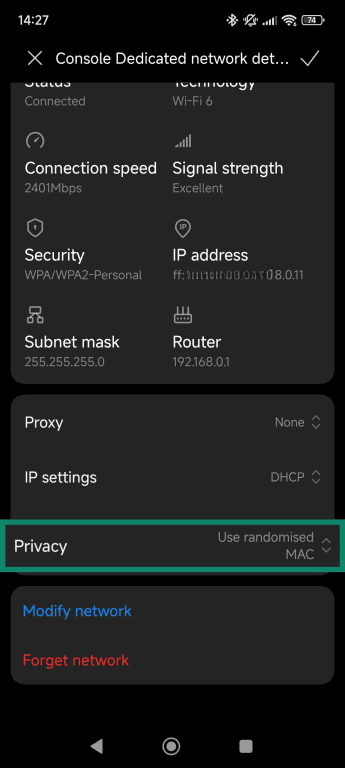
- Select Use randomized MAC if available.
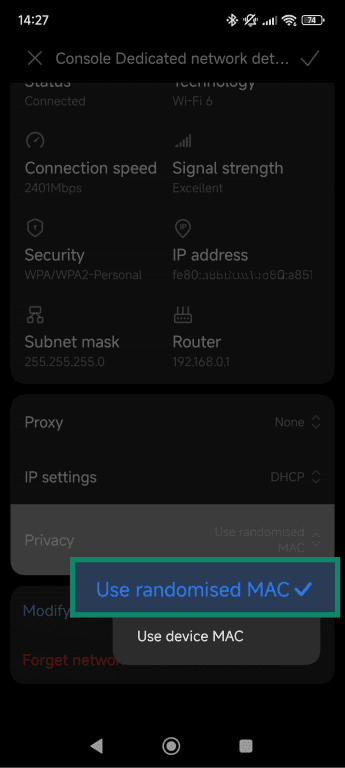
iOS
iOS doesn’t allow manual MAC address changes. It uses a built-in privacy feature called Private Addressing that creates a unique, randomized MAC address for each WiFi network you join.
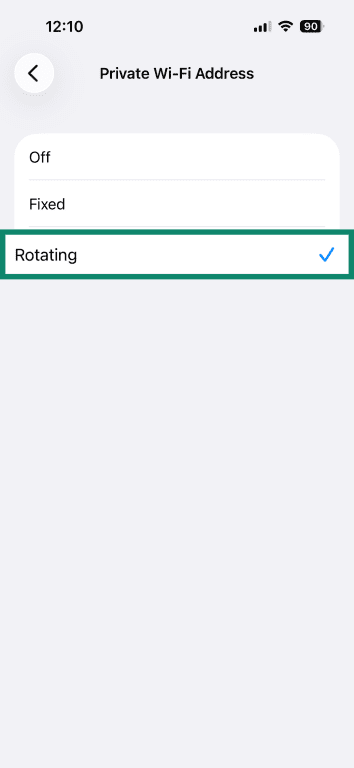
- Open Settings, tap Wi-Fi, and select the "i" icon beside your connected network.
- Access the Private Wi-Fi Address option and select Rotating.
Extra tips for protecting your MAC address
Protecting your MAC address is a key part of maintaining privacy on local networks. In addition to randomizing your MAC address, here are other practical steps you can take to limit tracking and reduce exposure:
- Turn off Wi-Fi when not in use: Disabling Wi-Fi stops your device from broadcasting its MAC address.
- Regularly update device firmware and software: Firmware and OS updates often include patches that fix vulnerabilities in network drivers and Wi-Fi components.
- Be cautious with MAC spoofing tools: These tools don’t modify hardware permanently, but using them incorrectly can break certain network features. Only use spoofing on trusted networks, and restore your original address when needed to avoid connection issues.
MAC filtering: Is it effective?
MAC filtering can restrict network access to approved addresses, but it isn’t a strong security measure on its own. Because MAC addresses can be easily spoofed, attackers can bypass these filters with relative ease.
While MAC filtering may add a small layer of protection, stronger access controls such as Wi-Fi Protected Access 3 (WPA3) encryption, 802.1X authentication, network segmentation, and virtual local area networks (VLANs) provide more reliable security for your network.
Does a VPN hide or change your MAC address?
A virtual private network (VPN) doesn’t hide or change your MAC address. Since the MAC address is used only for communication within your local network, it never leaves your device or local network environment. Because of this, the VPN cannot modify or mask it.
Instead, a VPN encrypts your internet traffic and routes it through a remote server, hiding your IP address and online activity from external observers. However, your local network devices (such as your router or modem) will still see your original MAC address.
What VPNs can and can’t do
A VPN can hide your IP address, encrypt your internet traffic, and make online activity harder to trace. It can’t change your MAC address or hide private (local) IP addresses from other devices on the same local network.
Additionally, a VPN doesn’t affect tracking systems that rely on hardware-level identifiers or information visible within your local network. To limit this kind of monitoring, you need device-level measures such as MAC address randomization, MAC spoofing, or disabling unused network interfaces.
FAQ: Common questions about MAC addresses
What is a MAC address on an iPhone?
A Media Access Control (MAC) address on an iPhone is a unique identifier for its network hardware. You can find the MAC address in the Wi-Fi settings, listed under Wi-Fi Address, which displays a series of six pairs of hexadecimal characters. This address helps the device communicate on local networks and can be randomized for privacy in newer iOS versions. Understanding this value is useful if you want to manage network permissions or reduce device tracking on public Wi-Fi.
Can you identify a device by its MAC address?
Yes, a Media Access Control (MAC) address can be used to identify a device within a local network. The first half of the address reveals the manufacturer, while the second half uniquely identifies the device itself. This makes it possible to track a device’s presence on Wi-Fi networks, though it doesn’t reveal personal information on its own. Combined with other identifiers, it can help network administrators manage or monitor connected hardware.
Does changing my MAC address improve privacy?
Changing Media Access Control (MAC) addresses can improve privacy on local networks. Randomizing or spoofing the address reduces tracking, making it harder for network operators or other devices to recognize your hardware. However, it only protects you from local network monitoring and doesn’t hide your activity on the wider internet. For full online privacy, additional tools like virtual private networks (VPNs) are recommended.
Can a VPN hide my MAC address?
No, a virtual private network (VPN) can’t hide your Media Access Control (MAC) address. A VPN changes your IP address and encrypts your internet traffic, which affects communication with websites and online services. Your MAC address stays visible to your router and any other device on the same local network. To hide or change it, you need randomization or spoofing at the device level.
Should I use a VPN and MAC spoofing together?
Using a virtual private network (VPN) and Media Access Control (MAC) spoofing together can maximize privacy. The VPN protects your IP address online, while a spoofed MAC address reduces the chance of tracking on local networks. This combination keeps your activity harder to trace both locally and online. It’s especially useful when connecting to public Wi-Fi, where devices and network operators could otherwise monitor your presence.
Take the first step to protect yourself online. Try ExpressVPN risk-free.
Get ExpressVPN