Are mobile hotspots secure? A complete guide to staying safe

Staying connected on the go has never been easier, thanks to mobile hotspots. Whether you’re tethering from your phone or using a portable Wi-Fi device, these tools offer fast and flexible internet access wherever you are.
But convenience can come at a cost: unsecured hotspots leave you vulnerable to cyberattacks.
In this guide, we’ll break down how mobile hotspots work, explore unsecured hotspot risks, and share simple, actionable steps to keep your connection safe.
What is a mobile hotspot?
A mobile hotspot (or cellular hotspot) lets you share a cellular internet connection with other devices by creating a private Wi-Fi network. Unlike home Wi-Fi, which comes from a fixed internet line and a router, a mobile hotspot uses cellular data from a phone plan or a dedicated mobile data plan to share internet wherever there’s cell signal.
There are two main types of mobile hotspots.
- Personal hotspots: Most smartphones can act as a mobile hotspot, sharing their mobile data with other devices, like your laptop or tablet. This is very convenient because you don’t need extra hardware, but it can use up your phone’s battery and data quickly.
- Portable Wi-Fi devices (dedicated hotspot devices): These are small, palm-sized devices that create their own Wi-Fi network. Designed specifically as mobile hotspots, they have a longer battery life, support more simultaneous connections, and provide more stable internet access. However, they require a separate data plan. They’re ideal for frequent travelers or anyone who wants to avoid draining their phone’s battery and data.
Some cell carriers offer mobile hotspot plans designed for heavier use. These can work with either your phone or a separate hotspot device and often give you more data and faster speeds than regular phone plans. They’re useful if you plan to use a hotspot regularly or for long periods.
How do mobile hotspots work?
In short, a mobile hotspot works by sharing internet access from a cellular connection with other devices over Wi-Fi. In other words, it’s like turning your phone (or portable Wi-Fi device) into a mini router.
The longer answer is that a mobile hotspot gets internet access from a cellular network, which is provided by your carrier through a SIM card and a mobile data plan. It then takes this cellular connection and broadcasts it as a Wi-Fi network that nearby devices can connect to. This process is called “tethering,” and any devices connected to the hotspot are known as “tethered devices.”
How to turn your phone into a personal hotspot
The exact steps to turn your phone into a personal hotspot may vary slightly depending on your software version, but here’s a general guide for Android and iOS.
On Android
- Open Settings and tap Connections.
- Scroll down and tap on Mobile Hotspot and Tethering.
- Toggle Mobile Hotspot on. Optionally, tap on Mobile Hotspot to adjust the settings, including the password.
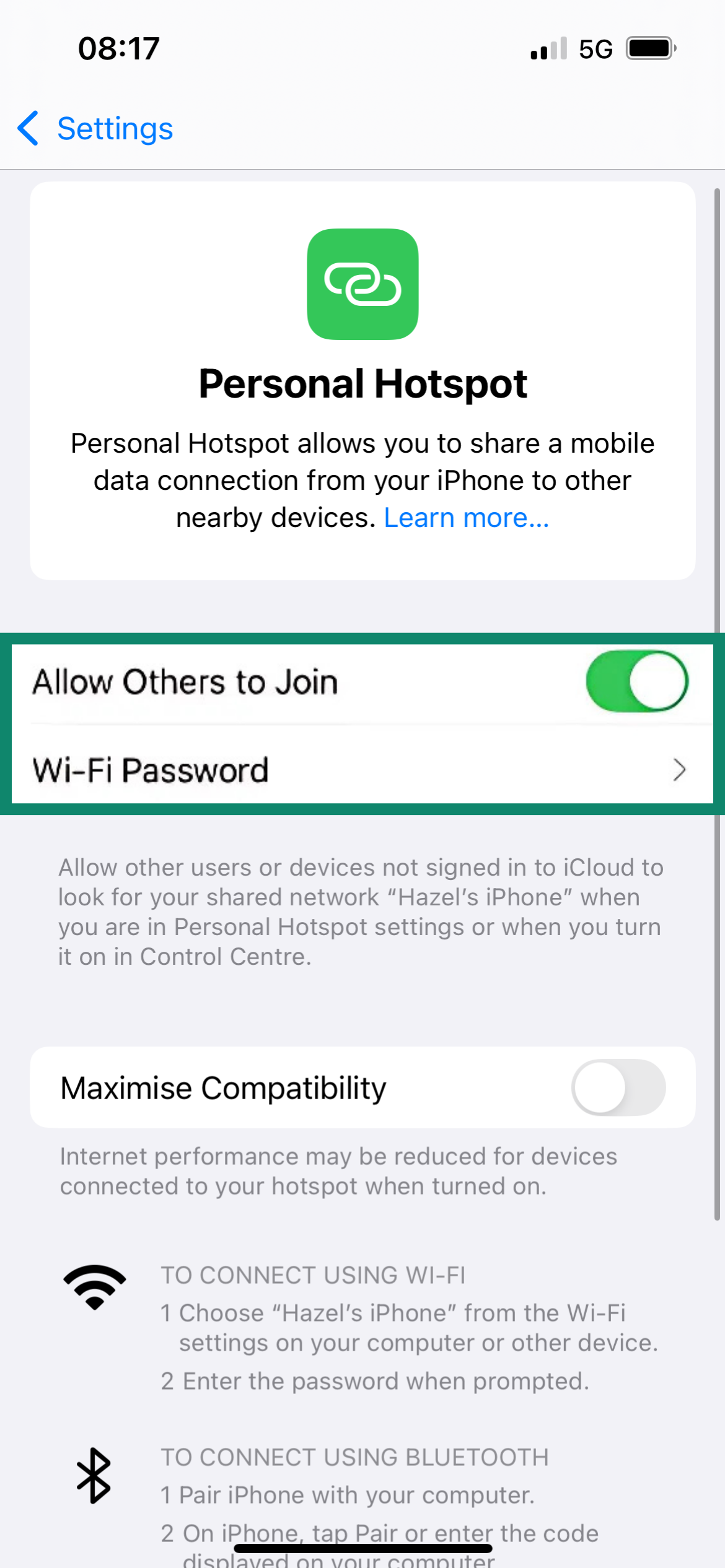
On iPhone
- Go to Settings > Personal Hotspot.
- Toggle Allow Others to Join, and that’s it! Optionally, you can change the Wi-Fi password to something more secure.
Common risks when using an unprotected hotspot
Using an unsecured mobile hotspot can expose your devices and data to serious risks. Here are some of the most common threats.
- Strangers using your data and bandwidth: If your hotspot has a weak password (or no password at all), anybody nearby can connect to your network. Strangers can use up your mobile data and slow down your connections.
- Malware infections: If any device on the network is infected with malware, it can spread to other devices on the same network. And if a threat actor manages to join your hotspot, they could attempt to install malware on your device to steal data, spy on you, or lock down your files with ransomware.
- Packet sniffing: Cybercriminals can intercept the traffic flowing through your hotspot using simple tools. This technique, called “packet sniffing,” allows them to “listen in” on your activity and can potentially expose sensitive data like the domains you’re visiting or, in case the website is not using HTTPS, your login credentials, emails, or payment details.
- Man-in-the-middle (MITM) attacks: This is when an attacker positions themselves between your mobile hotspot and connected devices. It allows them to monitor all traffic passing through your network and even redirect you to fake websites designed to steal your data or infect your device with malware.
How to secure your mobile hotspot
An unsecured hotspot makes your network vulnerable to unauthorized access and cyberattacks. Fortunately, it only takes a few simple steps to lock down your connection and protect your devices.
Set a strong and unique password
When you first enable your mobile hotspot, your device automatically creates a password. Often, these default passwords are weak and easy for threat actors to guess using brute-force cracking tools.
A good password should be lengthy and unique, ideally with an amalgamation of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols. If you share your password with others who want to tether to your network, it’s also a good idea to change up your password often to limit who has access and possibly also limit the number of devices that can connect to your hotspot.
The easiest way to get a strong password is by using a reliable password manager like ExpressKeys, which can also store and autofill your passwords.
Rename your SSID to something anonymous
Your Service Set Identifier (SSID), or the name of your Wi-Fi network, is visible to anyone nearby scanning for wireless networks. If the SSID includes personal information (like your name or phone model), it could make you an easier target for cybercriminals.
Enable WPA3 or WPA2 encryption
Your mobile hotspot should have some form of encryption set up by default. Encryption scrambles all data sent between your hotspot and connected devices to make it unreadable to others.
However, encryption strengths vary depending on the encryption standard. Avoid using outdated ones like Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP). Always choose Wi-Fi Protected Access 3 (WPA3) if your device supports it, as it’s currently the most secure encryption type available. If WPA3 isn’t available, WPA2 is also a reliable option.
Use a virtual private network (VPN) for additional privacy
Even with a secure password and encryption enabled, your internet traffic still travels over your carrier’s network and could be visible to them or cybercriminals. A VPN adds another layer of protection by encrypting all traffic from your device. This is especially useful when you’re using your hotspot in public places like cafes, airports, or hotels, where the risk of cyberattacks is higher.
We recommend installing a trusted VPN app on all devices you connect to your hotspot for the most protection. ExpressVPN has excellent Android and iOS apps that are easy to set up and use.
Turn off auto-connect and broadcasting when not in use
Leaving your hotspot on when you’re not using it isn’t just a drain on your battery and data; it’s also a security risk. When enabled, your phone is visible to anyone nearby, which makes it more vulnerable to threat actors.
Additionally, both Android and iOS phones have auto-connect features that can automatically turn on your phone’s hotspot and share your internet connection with trusted devices. While this might be convenient, it also means your hotspot could start broadcasting without your knowledge. For maximum security, it’s best to turn these features off.
Additional security best practices
Here are some additional tips for strengthening your mobile hotspot security.
How to monitor and control connected devices
Keeping track of which devices are connected to your hotspot can help you detect unauthorized users. Most smartphones and dedicated hotspot devices let you see a list of connected devices in their settings.
Some phone models allow you to disconnect a specific device, which also adds it to your blocklist, but this is not universal. If your phone doesn’t have this option, you can temporarily turn off your hotspot and change the password. This will disconnect all devices connected to your hotspot, so you’ll have to reconnect your own devices using the new password.
If you’re not satisfied with the amount of information or management options offered by your phone, consider downloading a reputable network scanner, like Fing.
Keeping your OS and firmware updated for hotspot safety
Security vulnerabilities in your phone’s operating system or a portable hotspot device’s firmware can create openings for attackers. Manufacturers frequently release updates to patch these weaknesses, so it’s crucial to keep your smartphone’s OS and any portable Wi-Fi devices you use up to date.
FAQ: Common questions about mobile hotspot security
Can someone hack my phone through my hotspot?
Yes, if your hotspot isn’t properly secured, cybercriminals can use it to gain access to your phone or other devices on the network. This might allow them to infect your device with malware, monitor your online activity, and steal sensitive data, like your login credentials or payment details.
Is a hotspot safer than public Wi-Fi?
Mobile hotspots are generally much safer than public Wi-Fi because you have full control over them, including the security settings and who can connect. In contrast, public Wi-Fi networks are often open to anyone nearby and have weak or no encryption. That said, hotspots aren’t immune to cyberattacks.
However, an unsecured mobile hotspot leaves you vulnerable to many of the same risks as public Wi-Fi, including unauthorized access, data interception, and other cyber threats.
Can people steal data through my hotspot?
Yes, if an unauthorized user manages to connect to your hotspot, they can potentially steal your data by listening in on your traffic, installing spyware on your device, or redirecting you to phishing sites.
Should I use a VPN on top of hotspot security?
Yes, using a VPN is highly recommended even when using a secured hotspot. Without a VPN, some of your data can still be seen by your phone carrier and potentially by cybercriminals. A VPN prevents this from happening by encrypting all traffic leaving your device, making it unreadable to third parties.
What are the downsides of using a personal hotspot?
Using your phone as a hotspot can drain its battery quickly and eat into your mobile data plan. It can also lead to slower speeds and less stable connections when under heavy use. Additionally, some carriers impose limits or extra charges on tethering, so it’s important to check the terms and conditions on your plan. This is why some people use a dedicated hotspot device instead.
How safe is a mobile hotspot?
A mobile hotspot can be very safe if configured properly. This means setting a strong, unique password, renaming your network to something anonymous, enabling Wi-Fi Protected Access 3 (WPA3) or WPA2 encryption, using a VPN, and turning off auto-connect and broadcasting when you’re not using the hotspot.
What encryption methods do mobile hotspots use?
Most modern mobile hotspots use Wi-Fi Protected Access 2 (WPA2) or WPA3 encryption to secure the network. WPA3 is the latest standard and offers improved security features over WPA2, including better defenses against password-guessing attacks. Whenever possible, use WPA3 to ensure the highest level of protection, and avoid outdated standards, like Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP).
Take the first step to protect yourself online. Try ExpressVPN risk-free.
Get ExpressVPN














Comments
"Thank you for this invaluable guide! Mobile hotspots are a lifeline for staying connected on the go, but security concerns have always nagged at the back of my mind. Your article provided a comprehensive rundown of practical steps to keep my mobile hotspot secure. From using strong passwords to enabling encryption, I now feel much more confident in protecting my data while staying connected. Thanks for empowering us with the knowledge to safeguard our digital lives!"
On the Android app, is there a way to ensure/force the hotspot connection through the VPN connection on the android device seperately from the device?
I have been in touch with ExpressVPN tech support for this exact issue. The answer is no. If you read the article carefully you'll notice that they ask you to "use a VPN on both the phone and the device you’re connecting to it", meaning that you need two VPN connections instead of a single one. The alternatives are a proxy app or rooting your phone.