How to increase bandwidth when using a VPN: Complete guide

Bandwidth is an important but often misunderstood metric that affects overall internet speed. While many people think bandwidth refers to the speed of their internet connection, it’s actually a distinct concept. Having a firm grasp of what bandwidth is (and what it isn’t) is important if you want to understand why your internet speeds are what they are.
This guide will explain what bandwidth is, what you can do to improve it, and how to get the best speeds while using a VPN.
What is bandwidth?
Bandwidth refers to the maximum amount of data that can flow through a network over a given period of time. When you browse the web or download files, your network has a limited capacity for moving data. This is usually measured in megabits per second (Mbps); it reflects how many bits of data can be transferred per second.
It’s important to remember that bandwidth usually applies to an entire network, not a specific device. A household with many online devices will require more bandwidth than one with a single laptop because every device takes a share of the available capacity.
Bandwidth vs. speed: Key differences
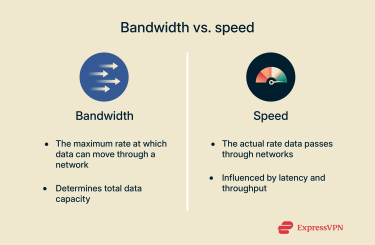 To elaborate on the distinction between bandwidth and speed, bandwidth is usually measured as the amount of data that a network can handle in one second, while speed is a more general term covering how much data a connection actually handles over a given period.
To elaborate on the distinction between bandwidth and speed, bandwidth is usually measured as the amount of data that a network can handle in one second, while speed is a more general term covering how much data a connection actually handles over a given period.
In networking, bandwidth dictates network capacity, whereas latency and throughput describe how much data a device processes in practice. Specifically, latency is the time it takes for a single data packet to travel between its source and destination, and throughput is the actual amount of data successfully delivered in one second.
People often use the word bandwidth when they’re actually referring to speed, latency, or throughput. Though the terms are closely related and all speak to general performance, they are not the same.
If your internet service provider (ISP) advertises up to 500Mbps, that figure refers to bandwidth, meaning your network’s theoretical maximum. It does not mean that your device will always achieve that much throughput. Additionally, if more than one device is connected to the network, they’ll have to split that total bandwidth between them.
Keep in mind that you can only change your home network’s bandwidth by contacting your ISP and upgrading your plan. In contrast, it’s normal for your actual internet speed to vary minute-to-minute and hour-to-hour.
How a VPN affects bandwidth
First off, it’s important to note that using a VPN will not have any effect on your network’s overall bandwidth. That said, using a VPN can affect a device’s internet speed. For various reasons, using a VPN may reduce a device's throughput or effective bandwidth.
Why VPNs can change your effective bandwidth
When you use a VPN, your traffic is encrypted and routed through a remote server before reaching its destination. This extra step adds latency and reduces throughput. Encryption also requires processing time on both your device and the VPN server, and the routing adds distance and potential congestion.
The result of this is a reduction in your effective bandwidth. However, in some situations, a VPN may improve throughput. ISPs and some network admins can intentionally slow users’ connections, a practice known as throttling. For example, an ISP may reduce bandwidth for specific types of traffic, such as high-resolution video streaming.
In such cases, using a VPN could help maintain more consistent speeds by preventing the ISP from seeing the type of content being accessed. That said, a VPN won’t help if your connection is slowed due to other factors, such as exceeding a data cap, network congestion, or overall bandwidth limitation.
Effects of VPN server distance, congestion, and protocol
The physical distance between a device and the VPN server it connects to influences the connected device’s effective speed. All data you send and receive travels from your device, to the VPN server, and then back. If the server is far away, this can add latency, which negatively impacts performance.
In addition to its location, a server’s congestion may also affect the speed users experience while connected. VPN servers have their own bandwidth, so if more users are connected, this can result in slower speeds for everyone.
Lastly, the VPN protocol you use will also affect your speed while connected. For example, Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol (L2TP) is very fast, but this is mostly because it doesn’t include any encryption by default. VPN users need to balance speed, security, and reliability when choosing a protocol.
Quick fixes to improve VPN bandwidth
Here are several quick fixes that, depending on the circumstances, may improve your effective bandwidth while using a VPN.
Switch to a closer VPN server
If you connect to a server across the world, your data travels a much greater distance to reach its destination and come back, which increases the delay. If speed is your priority, you should connect to a closer server.
Change VPN protocol
Protocols govern how your VPN tunnels data. Choosing the right one can make a noticeable difference in your performance. OpenVPN is widely used and generally achieves a good balance of speed and security.
That said, newer protocols with lightweight code, such as WireGuard and ExpressVPN’s Lightway, are generally faster. Windows users on Lightway can also activate Lightway Turbo, which incorporates multi-lane tunneling to send more data at once (increasing your effective bandwidth).
Some VPN clients support multiple protocols, so you may want to test them out to see which one provides you with the best speeds.
Restart VPN app and router
Restarting your VPN and router is a simple solution that can solve some speed and performance issues. Routers and VPN apps store temporary data and session information, which can become bloated over time. By clearing out temporary memory, resetting connections, and re-establishing optimal settings, power cycling may improve performance.
To reboot most routers, unplug them for at least sixty seconds, wait for their power to drain, and then plug them back in.
Schedule heavy usage outside peak hours
Network congestion occurs when too many users share the same infrastructure. Using internet infrastructure (VPN servers included) during peak hours may result in slower speeds.
While you can’t control what other people do, it may be possible to schedule bandwidth-heavy tasks for when your VPN’s servers are less busy. Some providers display each server’s current load or expected latency to make this easier. On its macOS, Windows, Android, and iOS apps, ExpressVPN allows you to run speed tests on its servers and see server latency and other performance data.
In the same vein, you’ll also experience better speeds when fewer devices are active on your home network.
More VPN bandwidth optimization strategies
Split tunneling
Split tunneling enables you to route traffic from specific apps through the encrypted VPN tunnel while others access the internet normally. By routing only sensitive data through the VPN, you reduce the encryption overhead and preserve bandwidth for activities that don’t require enhanced privacy.
For instance, you could set your browser and messaging app to use the VPN while routing traffic from a video game through your regular connection. By only adding encryption where necessary, you’ll keep more network and computational resources available.
Just remember that not every VPN provider offers this feature. Even if you choose one that does (like ExpressVPN), take care to ensure that all sensitive apps are set to use the VPN tunnel.
Use wired connections instead of Wi-Fi
Regardless of whether you’re using a VPN or not, connecting your devices using Ethernet cables rather than Wi-Fi usually improves throughput. Wireless signals travel through air, walls, and other obstacles, which introduces interference. As a result, wireless connections are generally slower and more variable.
Wired connections are generally faster and more reliable. Using Ethernet won’t increase the bandwidth your ISP allocates, but it may allow you to use that bandwidth more efficiently.
If you want to increase your network’s actual bandwidth, check whether your ISP offers fiber. These connections can accommodate greater data flows and are often tied to both higher bandwidth and better performance in practice.
Adjust VPN encryption level for speed vs. security
Encryption strength and performance are inversely related; higher levels of encryption provide more protection but require more processing time.
In addition to protocols, some VPNs allow you to choose between different ciphers and key lengths, making it possible to choose lower levels of encryption in an effort to reduce processing time.
Some VPNs also offer perfect forward secrecy, which changes encryption keys regularly. While this enhances security, it increases computational overhead. Evaluate your overall network performance and security needs before customizing your VPN’s encryption settings.
Limit devices and apps running through VPN
It may be a good idea to limit the number of devices that use a VPN to connect to the internet. Each device uses data regardless, but they consume even more bandwidth when connected to a VPN.
Identify which devices benefit from the extra protection provided by a VPN and which do not necessarily need to have their traffic encrypted. You may want to consider installing a VPN on your router, but this might encrypt the traffic of all of your devices.
To save bandwidth, some providers allow you to set device groups. This lets you, for example, exclude your smart fridge from the VPN tunnel, potentially increasing speeds on your other devices.
VPN service and hardware solutions

Choosing a VPN with high-speed servers
Due to both hardware and software factors, servers vary in terms of efficiency. When speed is a priority, look for a provider that operates a network of high-performance servers. Location matters too; if your provider doesn’t have servers near you, you’ll have to accept slower speeds. ExpressVPN provides ultra-fast servers in 105 countries across the globe, all of which can be connected to with Lightway or OpenVPN.
Keep in mind that free VPNs are more likely to have overcrowded servers than their paid counterparts. Some may slow connections once users reach a data limit. You’ll want to make sure that your provider offers unlimited bandwidth and has a strong maintenance team that can deal with technical issues and hardware faults.
Note: Performance aside, you may also want to consider how a provider you’re considering handles server logs. To provide greater privacy, ExpressVPN and certain other providers work under no-logs policies.
Invest in a high-performance router for VPN usage
Even if your ISP allocates you enough bandwidth, there’s a chance that your router can’t handle that amount of data. As technology advances, older routers struggle to keep up with modern data demands and an increased number of devices.
Upgrading your router can provide a noticeable speed boost, especially if you have many devices connected. Choose a router with a powerful processor, sufficient memory, and support for VPN pass-through or client functionality. Some routers even allow you to install VPN firmware directly, so the VPN can protect your entire home network.
Upgrade your internet plan if necessary
If your plan doesn’t provide enough bandwidth for your household’s needs, your devices will compete for every scrap of capacity. If this is the case, reaching out to your ISP and upgrading your internet plan is the only real option.
Tools for monitoring and testing your VPN bandwidth
The only way to tell if your performance is matching up with your maximum bandwidth is to run tests using the right tools.
How to compare bandwidth with and without a VPN
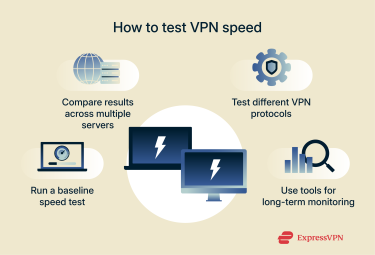 You can compare your bandwidth with and without a VPN by running a simple test using an online tool like Ookla. Start off by making sure none of your devices are connected to a VPN server. Run a baseline speed test without the VPN to see how fast your unencrypted speeds are.
You can compare your bandwidth with and without a VPN by running a simple test using an online tool like Ookla. Start off by making sure none of your devices are connected to a VPN server. Run a baseline speed test without the VPN to see how fast your unencrypted speeds are.
It’s important to record your results so you can make accurate comparisons. Take a screenshot or note the download speed, upload speed, and latency that the test recorded. You may also want to run two or three sample tests to determine your normal range, recording each result.
Once you have your baseline performance, connect to a nearby VPN server and run the test again. As with your baseline tests, it’s a good idea to do multiple tests while connected to the VPN.
If your VPN noticeably slows down your connection, investigate your server selection, VPN protocol, and potential hardware limitations to find the source of the problem. Remember that some slowdown is normal because of the encryption process, but it shouldn’t have a significant impact on your browsing or streaming experience.
In-depth testing
For the best results, perform multiple tests across different VPN server locations while using various protocols. Recording and reviewing the results of these tests should give you a clear picture of how a VPN affects your speed. It may also highlight which servers and protocols provide the best performance for you and your network. Just remember that security is also an important factor that speed tests won’t account for.
If the results are still inconclusive, consider long-term monitoring software or router-based monitoring to track your performance over time. Real-time monitoring may reveal patterns and potential adjustments you can make, allowing you to get the most out of your VPN connection.
FAQ: Common questions about bandwidth and VPNs
Does a VPN decrease my bandwidth?
Using a VPN adds encryption and routing overhead, which somewhat reduces your available or effective bandwidth. Top-tier VPNs, like ExpressVPN, use efficient protocols like Lightway and offer a large server network to maintain high performance with minimal drops in speed, but all VPNs will slightly reduce your bandwidth. The amount of reduction depends on server distance, VPN protocol, and hardware.
How can I speed up my VPN connection?
You can speed up your VPN by connecting to a nearby server; closer servers typically have reduced latency. Depending on the VPN, you can try switching to a faster protocol, too. You can also restart your router to clear temporary memory and close any unnecessary applications.
Which VPN protocol gives me the best bandwidth?
WireGuard or Lightway generally offer the best performance because of their streamlined design and modern cryptography. Internet Key Exchange version 2 (IKEv2) is efficient for mobile devices, and OpenVPN in User Datagram Protocol (UDP) mode provides a good balance of speed and security.
Can a free VPN affect my internet speed?
All VPNs can affect internet speeds to some extent, and free services often have a greater impact. Some may impose data caps or reduce speeds after a certain amount of usage. Server congestion can also play a role. Free VPNs typically have fewer servers and more users, which can lead to slower performance at times.
What is the best way to test VPN bandwidth?
Run baseline speed tests without the VPN and then repeat the tests with the VPN turned on. Test multiple servers and protocols to figure out what works best for you.
Can I increase my bandwidth beyond my ISP’s limits?
No. Your bandwidth ceiling is determined by your internet service provider's (ISP’s) infrastructure and available internet plans.
Take the first step to protect yourself online. Try ExpressVPN risk-free.
Get ExpressVPN